Introduction
An avalanche of recent publications (Zuboff, 2019; Gershenfeld, Gershenfeld & Gershenfeld, 2017; Carr, 2010; Lovelock, 2019; and Tegmark, 2017) reflect the emotional range of our current obsessions about the Digital Economy, which are concerned, respectively, with: its inherent capacity for surveillance, domination, and control; its opportunities for extending the powers of digital fabrication systems to all members of the community; its retarding effects on deep concept formation and long-term memory; the prospect of being watched over by “machines of loving grace” that control our energy grids, transport and weapon systems; and, the limitless prospects for the evolution of AI, through procedures of “recursive self-improvement”. In my own contribution to the analysis of the digital economy (Juniper, 2018), I discuss machine learning and AI from a philosophical perspective that is informed by Marx, Schelling, Peirce and Steigler, arguing for the development of new semantic technologies based on diagrammatic reasoning, that could provide users with more insight and control over applications.[1]
AI and Machine Learning practitioners have also embraced the new technology of Deep Learning Convolution Neural Networks (DLCNNs), Recursive Neural Networks, and Reservoir Neural Networks with a mixture of both hubris and concern[2]. In an influential 2008 article in Wired magazine, Chris Anderson claimed that these new techniques no longer required a resort to scientific theories, hypotheses, or processes of causal inference because the data effectively “speak for themselves”. In his response to Anderson’s claims, Mazzochi (2015) has observed that although the new approaches to machine learning have certainly increased our capacity to find patterns (which are often non-linear in nature), correlations are not all there is to know. Mazzochi insists that they cannot tell us precisely why something is happening, although they may alert us to the fact that something may be happening. Likewise, Kitchin (2014) complains that the data never “speak for themselves”, as they shaped by the platform, data ontology, chosen algorithms and so forth. Moreover, not only do scientists have to explain the “what”, they also have to explain the “why”. For Lin (2015) the whole debate reflects a confusion between the specific goal of (i) better science; and that of, (ii) better engineering (understood in computational terms). While the first goal may be helpful, it is certainly not necessary for the second, which he argues has certainly been furthered by the emerging deep-learning techniques[3].
In what follows, I want to briefly evaluate these new approaches to machine learning, from the perspective of a Post Keynesian economist, in terms of how they could specifically contribute to a deeper understanding of macroeconomic analysis. To this end, I shall investigate thoughtful explanations for the “unreasonable effectiveness” of deep-learning techniques, which will therefore focus on the modelling, estimation, and (decentralised) control of system (-of systems) rather than image classification or natural language processing.
The “Unreasonable effectiveness” of the New AI
Machine learning is but one aspect of Artificial Intelligence. In the 1980s, DARPA temporarily withdrew funding for US research in this field because it wasn’t delivering on what it had promised. Rodney Brooks has explained that this stumbling block was overcome by the development of the New AI, which coincided with the development of Deep Learning techniques characterised by very large neural networks featuring multiple hidden layers and weight sharing. In Brooks’ case, the reasoning behind his own contributions to the New AI were based on the straightforward idea that previous efforts had foundered on the attempt to combine perception, action, and logical inference “subsystems” into one integrated system. Accordingly, logical “inference engines” were removed from the whole process so that system developers and software engineers could just focus on more straightforward modules for perception and action. Intelligence would then arise spontaneously at the intersection between perception and action in a decentralized, but effective manner.
One example of this would be the ability of social media to classify and label images. Donald Trump could then, perhaps, be informed about those images having the greatest influence over his constituency, without worrying about the truth-content that may be possessed by any of the individual images (see Bengio et al., 2014, for a technical overview of this machine learning capability). Another example of relevance to the research of Brooks, would be an autonomous rover navigating its way along a Martian dust plain, that is confronted by a large rock in its path. Actuators and motors could then move the rover away from the obstacle so that it could once again advance unimpeded along its chosen trajectory—this would be a clear instance of decentralized intelligence!
In their efforts to explain the effectiveness of machine learning in a natural science context, Lin, Tegmark, and Rodnick (2017), consider the capacity of deep learning techniques in reproducing Truncated Taylor series for Hamiltonians. As Poggio et al., (2017) demonstrate, this can be accomplished because a multi-layered neural network can be formally interpreted as a machine representing a function of functions of functions… :
e.g.
At the end of the chain we arrive at simple, localized functions, with more general and global functions situated at higher levels in the hierarchy. Lin, Tegmark, and Rodnick (2017) observe that this formalism would suffice for the representation of a range of simple polynomials that are to be found in the mathematical physics literature (of degree 2-4 for the Navier-Stokes equations or Maxwell’s equations). They explain why such simple polynomials characterise a range of empirically observable phenomena in the physical sciences, in terms of three dominant features, namely: sparseness, symmetry, and low-order[4]. Poggio et al., (2017) examine this polynomial approximating ability of DLCNNs, also noting that sparse polynomials are easier to learn than generic ones owing to the parsimonious number of terms, trainable parameters, and the associated VC dimension of the equations (which are all exponential in the number of variables). The same thing applies to highly variable Boolean functions (in the sense of having high frequencies in their Fourier spectrum). Lin, Tegmark, and Rodnick (2017) go on to consider noise from a cosmological perspective, noting that background radiation, operating as a potential source of perturbations to an observed system, can be described as a relatively well-behaved Markov process.
In both of these cases, we can discern nothing that is strictly comparable with the dynamics Post Keynesian theory, once we have abandoned the Ramsey-Keynes (i.e. neoclassical) growth model as the driver of long -run behaviour in a macroeconomy. From a Post Keynesian perspective, the macroeconomy can only ever be provisionally described by a system of differential equations characterised by well-behaved asymptotic properties of convergence to a unique and stable equilibrium.
The Macroeconomy from a Post Keynesian Perspective:
In The General Theory, Keynes (1936) argued that short-run equilibrium could be described by the “Point of Effective Demand”, which occurs in remuneration-employment space, at the point of intersection between aggregate expenditure ( in the form of expected proceeds associated with a certain level of employment) and aggregate supply (in the form of actual proceeds elicited by certain level of employment). At this point of intersection, the expectation of proceeds formed by firms in aggregate is fulfilled, so that there is no incentive for firms to change their existing offers of employment. However, this can occur at a variety of different levels of employment (and thus unemployment).
For Keynes, short-run equilibrium is conceived in terms of a simple metaphor of a glass rolling on a table rather than that of a ball rolling along in a smooth bowl with a clearly defined minimum. When it comes to the determination of adjustments to some long-run full-employment equilibrium, Keynes was no less skeptical. Against the “Treasury-line” of Arthur Pigou, Keynes argued that there were no “automatic stabilizers” that could come into operation. Pigou claimed that with rising unemployment wages would begin to fall, and prices along with them. This would make consumers and firms wealthier in real terms, occasioning a rise in aggregate levels of spending. Instead, Keynes insisted that two other negative influences would come into play, detracting from growth. First, he introduced Irving Fisher’s notion of debt-deflation. According to Fisher’s theory, falling prices would transfer income from high-spending borrowers to low-spending lenders, because each agent was locked in to nominal rather than real or indexed contracts. Second, the increasing uncertainty occasioned by falling aggregate demand and employment, would increase the preference for liquid assets across the liquidity spectrum ranging from money or near-money (the most liquid), through short-term fixed interest securities through to long-term fixed interest securities and equities and, ultimately, physical plant and equipment (the least liquid of assets).
In formal terms, the uncertainty responsible for this phenomenon of liquidity preference can be represented by decision-making techniques based on multiple priors, sub-additive distributions, or fuzzy measure theory (Juniper, 2005). Let us take the first of these formalisms, incorporated into contemporary models of risk-sensitive control in systems characterised by a stochastic uncertainty constraint (measuring the gap between free and bound entropy) accounting for some composite of observation error, external perturbations, and model uncertainty. While the stochastic uncertainty constraint can be interpreted in ontological terms as one representing currently unknown but potentially knowable information (i.e. ambiguity), it can also be interpreted in terms of information that could never be known (i.e. fundamental uncertainty). For Keynes, calculations of expected returns were mere “conventions” designed to calm our disquietude, but they could never remove uncertainty by converting it into certainty equivalents.
Another source of both short-run and long-run departure from equilibrium has been described in Hyman Minsky’s (1992) analysis of Financial Instability, which was heavily influenced by both Keynes Michal Kalecki. As the economy began to recover from a period of crisis or instability, Minsky argued that endogenous forces would come into play that would eventually drive the system back into crisis. Stability would gradually be transformed into instability and crisis. On the return to a stable expansion path, after firms and households had repaired their balance-sheet structures, financial fragility would begin to increase as agents steadily came to rely more on external sources of finance, as firms began to defer the break-even times of their investment projects, and as overall levels of diversification in the economy steadily came to be eroded (see Barwell and Burrows, 2011, for an influential Bank of England study of Minskyian financial instability). Minsky saw securitization (e.g. in the form of collateralized debt obligations etc.) as an additional source of fragility due to its corrosive effects on the underwriting system (effects that could never be entirely tamed through a resort to credit default swaps or more sophisticated hedging procedures). For Minsky, conditions of fragility, established preceding and during a crisis may only be partially overcome in the recovery stage, thus becoming responsible for ever deeper (hysteric) crises in the future[5].
An additional, perhaps more fundamental, reason for long-run instability is revealed by Piero Sraffa’s (1960) insights into the structural nature of shifts in the patterns of accumulation, within a multisectoral economy, as embodied in the notion of an invariant standard of value. Sraffa interprets David Ricardo’s quest for a standard commodity—one whose value would not change when the distribution of income between wages and profits was allowed to vary—as a quest that was ultimately self-defeating. This is because any standard commodity would have to be formally constructed with weights determined by the eigenvalue-structure of the input-output matrix. Nevertheless, changes in income distribution would lead to shifts in the composition of demand that, in turn would induce increasing or decreasing returns to scale. This would feed back onto the eigen-value structure of the input-output matrix, in turn requiring the calculation of another standard commodity (see Andrews, 2015, and Martins, 2019, for interpretations of Sraffa advanced along these lines). If we return to the case of the neoclassical growth model, Sraffa’s contribution to the debates in capital theory has completely undermined any notion of an optimal or “natural rate of interest” (Sraffa, 1960; Burmeister, 2000). From a policy perspective, this justifies an “anchoring” role for government policy interventions which aim to provide for both stability and greater equity in regard to both the minimum-wage (as an anchor for wage relativities) and determination of the overnight or ‘target’ rate of interest (as an anchor for relative rates-of-return).
From a modelling perspective, Martins (2019) insists that Sraffa drew a sharp distinction between a notion of ‘logical’ time (which is of relevance to the determination of “reproduction prices” on the basis of the labour theory of value, on the basis of a “snapshot” characterization of current input-output relations) and it’s counterpart, historical time (which is of relevance to the determination of social norms such as the subsistence wage, or policies of dividend-retention). When constructing stock-flow-consistent macroeconomic model this same distinction carries over to the historical determination of key stock-flow norms, which govern long-run behaviour in the model. Of course, in a long-run macroeconomic setting, fiscal and monetary policy interventions are also crucial inputs into the calculation of benchmark rates of accumulation (a feature which serves to distinguish these Post-Keynesian models from their neoclassical counterparts).[6]
Machine Learning and Fixed-point Theorems
In this paper’s discussion of macroeconomic phenomena, I have chosen to focus heavily on the determinants of movements away from stable, unique equilibria, in both the short-run and the long-run. Notions of equilibrium are central to issues of effectiveness in both econometrics and machine-learning. Of pertinence to the former, is the technique of cointegration and error-correction modelling. While the cointegrating vector represents a long-equilibrium, the error-correction process represents adjustment towards this equilibrium. In a machine-learning context, presumptions of equilibrium underpin a variety of fixed-point theorems that play a crucial role in: (i) techniques of data reduction; (ii) efforts to eliminate redundancy within the network itself with the ultimate aim of overcoming the infamous “curse of dimensionality”, while preserving “richness of interaction”; and, (iii) the optimal tuning of parameters (and hyper-parameters that govern the overall model architecture). Specific techniques of data compression, such as Randomized Numerical Linear Algebra (Drineas and Mahoney, 2017), rely on mathematical techniques such as Moore-Penrose inverses and Tikhanov regularization theory (Barata and Hussein, 2011). Notions of optimization are a critical element in the application of these techniques. This applies, especially, to the gradient descent algorithms that are deployed for the tuning of parameters (and sometimes hyper-parameters) within the neural network. Techniques of tensor contraction and singular value decomposition are also drawn upon for dimensionality reduction is complex tensor networks (Cichoki et al., 2016, 2017). Wherever and whenever optimization techniques are required, some kind of fixed-point theorem comes into play. The relationship between fixed-point theorems, asymptotic theory, and notions of equilibrium in complex systems is not straightforward. See both Prokopenko et al., 2019 and Yanofsky, 2003, for a wide-ranging discussion of this issue, which opens onto a discussion of many inter-related “paradoxes of self-referentiality”.
For example, a highly-specialized literature on neural tangent kernels focuses on how kernel-based techniques can be applied in a machine learning context, to ensure that local rather than global maxima or minima are avoided during the whole process of gradient descent (see Yang, 2019). Here, the invariant characteristics of the kernel guarantee that tuning would satisfy certain robustness properties. An associated body of research on the tuning of parameters at the “edge of chaos”, highlights the importance of applying optimization algorithms close to the boundary of, but never within the chaotic region of dynamic flow (see Bietti and Mairal 2019, and Bertschinger and Natschläger, 2004). There are subtle formal linkages between the properties of neural tangent kernels and notions of optimization at the edge-of-chaos that I am unable to do justice to in this paper.
From a Post Keynesian perspective and despite this evolution in our understanding of optimization in a machine learning context, it would seem that efforts to apply the existing panoply of deep learning techniques may be thwarted by contrariwise aspects of the behaviour of dynamic macroeconomic system. For macroeconomists working with Real Business Cycle Models and their derivatives, none of this is seen as a problem because unreasonably-behaved dynamics are usually precluded by assumption. Although perturbations are seen to drive the business cycle in these models, agents are assumed to make optimal use of information, in the full knowledge of how the economy operates, so that government interventions simply pull the economy further away from equilibrium by adding more noise to the system. Although more recent dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) models allow for various forms of market failure, notions of long-run equilibrium still play a fundamental role[7]. Instead, in a more realistic, Post Keynesian world, optimization algorithms would have to work very hard in their pursuit of what amounts to a “will-o-the-wisp”: namely, a system characterised by processes of shifting and non-stationary (hysteretic) equilibria[8].
Differential Programming
Recent discussions of machine learning and AI, have emphasized the significance of developments in differential programming. Yann LeCun (2018), one of the major contributors to the new Deep learning paradigm has noted that,
An increasingly large number of people are defining the networks procedurally in a data-dependent way (with loops and conditionals), allowing them to change dynamically as a function of the input data fed to them. It’s really very much like a regular program, except it’s parameterized, automatically differentiated, and trainable/optimizable.
One way of understanding this approach is to think of something that is a cross between a dynamic network of nodes and edges and a spread sheet. Each node contains a variety of functional formulas that draw on the inputs from other nodes and provides outputs that in turn, either feed into other nodes or can be observed by scopes. However, techniques of backpropagation and automatic differentiation can be applied to the entire network (using the chain rule while unfurling each of the paths in the network on the basis of Taylors series representations of each formula). This capability promises to overcome the limitations of econometric techniques when it comes to the estimation of large-scale models. For example, techniques of structural vector autoregression, which are multivariate extensions to univariate error-correction modelling techniques can only be applied to highly parsimonious, small-scale systems of equations.
Based on the initial work of Ehrhard and Regnier (2003), a flurry of research papers now deal with extensions to functional programming techniques to account for partial derivatives (Plotkin, 2020), higher-order differentiation and tensor calculus on manifolds (Cruttwell, Gallagher, & MacAdam, 2019), how best to account for computational effects (which are described in Rivas, 2018), and industrial-scale software engineering (The Statebox Team, 2019). Members of the functional programming and applied category theory community have drawn on the notion of a lens, as means for accommodating the bidirectional[9] nature of backpropagation[10] (Clarke et al., 2020; Spivak, 2019; Fong, Spivak and Tuyéras, 2017).
Conclusion
The potential flexibility and power of differential programming, could usher in a new era of policy-driven modelling, by allowing researchers to combine (i) traditionally aggregative macroeconomic models with multi-sectoral models of price and output determination (e.g. stock-flow-consistent Post Keynesian models and Sraffian or Marxian models of inter-sectoral production relationships); discrete-time and continuous-time models (i.e. hybrid systems represented integro-differential equations), and both linear and non-linear dynamics. This would clearly support efforts to develop more realistic models of economic phenomena.
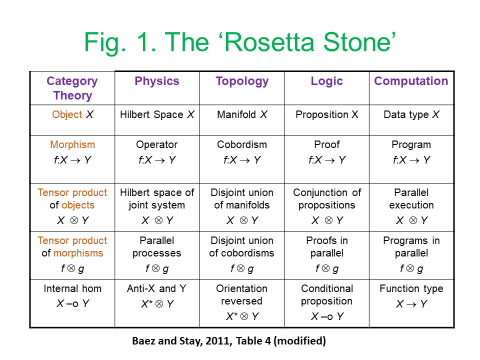
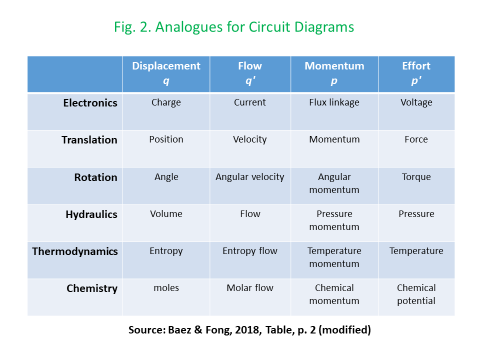
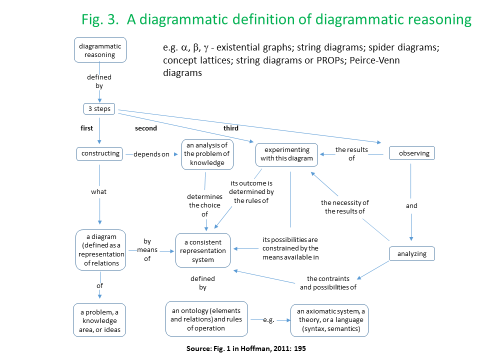
The development of network-based models of dynamic systems has been given impetus by research in three main domains: brain science imaging, quantum tensor networks, and Geographical Information Systems in each case, tensor analysis of multiple-input and multiple-output nodes has played a key role. In each of these cases, the complexity associated with tensor algebra has been ameliorated by the deployment of diagrammatic techniques based on the respective use of Markov-Penrose’ diagrams, the diagrammatic Z-X calculus, and the development of “region-” rather than “point”-based topologies and mereologies. These same diagrammatic techniques have been taken up by the Applied Category Theory community to achieve both a deeper and more user-friendly understanding of lenses and other optics (Boisseau, 2020; Riley, 2018), alongside diagrammatic approaches to simply-typed, differential, and integral, versions of the lambda calculus (Lemay, 2017, Zeilberger and Giorgetti, 2015).
As I have argued, in more general terms, in Juniper (2018), the development of new software platforms based on diagrammatic reasoning could mean that differential programming techniques could potentially be disseminated to a much larger number of users who might have limited programming knowledge or skill (to some extent, today’s spreadsheets provide an example of this)[11]. In the case of AI, this could allow workers to regain control over machines which had previously either operated “behind their backs” or else, on the basis of highly specialized expertise. Improvements of this kind also have the potential to support higher levels of collaboration in innovation at the point-of-production. In the more restricted macroeconomic context, modelling could become less of a “black-box” and more of an “art” than a mystifying “science”. Diagrammatic approaches to modelling could help to make all of this more transparent. Of course, there are a lot of “coulds” in this paragraph. The development and use of technology can and should never be discussed in isolation form its political and organizational context. To a large extent, this political insight, was one of the main drivers and motivating forces for this paper.
[1] One intuitive way of thinking about this is that it would extend principles of “human centred manufacturing” into some of the more computational elements of the digital economy.
[2] See Christopher Olah’s blog entry for a helpful overview of various deep-learning architectures.
[3] For this reason, I will avoid any further discussion of convolution-based techniques and kernel methods, which have contributed, respectively, to rapid progress in image-classification and in applications of support-vector machines. An animated introduction to convolution-based techniques is provided by Cornellis (2018) while kernel-based techniques and the famous “kernel trick” deployed in support vector machines is lucidly described in Wright (2018). Rectified Linear Units or ReLU’s—the activation functions most commonly-used in deep learning neural networks—are examined in Brownlee (2019).
[4] The importance of symmetries in mathematical physics is examined in a recent paper by John Baez (2020), who investigates the source of symmetries in relation to Noether’s theorem.
[5] Some of these components of fragility, such as loss of diversification and deferment of breakeven times, would obviously be hard to capture in a highly aggregative macroeconomic model, but certain proxies could be constructed to this end.
[6] Of course, the rate at which labour—dead and living—is pulled out of production, also determines intra- and inter-sectoral economic performance, growth in trade, and overall rates of accumulation. It is also one of the key drivers of fundamental uncertainty for investors.
[7] See Stiglitz (2018) for a critical review of DSGE models, and Andrle and Solmaz (2017) for an empirical analysis of the business cycle, which raises doubts about the dynamic assumptions implied by a variety of macroeconomic models. The contribution of non-discretionary expenditure to instability in the business cycle has been highlighted by the recent Post Keynesian theoretical literature on the so-called “Sraffa super-multiplier” (Fiebiger, 2017; Fiebiger and Lavoie, 2017).
[8] Important sources of hysteresis, additional to those of a Minskyian nature, include those associated with rising unemployment, with its obvious impacts on physical and mental health, crime rates, and scarring in the eyes of prospective employers. Rates of innovation (and thus, productivity growth) are also adversely affected by declining levels of aggregate demand.
[9] The implementation function takes the vector of parameters and inputs and transforms them into outputs, while the request function takes parameters, inputs and outputs and emits a new set of inputs, whereas the update function takes parameters, inputs and outputs and transforms them into a new set of parameter values. Together, the update and request functions perform gradient descent with the request function passing back the inverted value of the gradient of total error with respect to the input. Each parameter is updated so that it moves a given step-size in the direction that most reduces the specified total error function
[10] For an introduction to some of the mathematical and programming-based techniques required for working with optics see Loregian (2019), Boisseau and Gibbons (2018), Culbertson and Kurtz (2013), and Román (2019).
[11] Software suites such as AlgebraicJulia and Statebox can already recognise the role of different types of string diagrams in representing networks, dynamical systems, and (in the latter case) commercial processes and transactions.